The maximum tolerable level of consumption of selected nutrients

Every nutrient supplied in the form of a dietary supplement or food has a specified safe maximum daily dose for consumption by humans.
Read More →
Every nutrient supplied in the form of a dietary supplement or food has a specified safe maximum daily dose for consumption by humans.
Read More →
The role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of the common cold has been a subject of controversy for at least 60 years.
Read More →
Covering 60 years of research without mentioning a paper that highlights flaws in the literature, in a review, should negate any conclusion.
Read More →
The Cochrane review by Douglas et al.[1], which is referenced in the Best Practice article by Douglas and Hemilä[2], covers 60 years of research into vitamin C and the common […]
Read More →
Bowel tolerance, the amount of ascorbic acid tolerated orally without producing diarrhea, increases with the toxicity of diseases.
Read More →
This paper presents a new account of the action of ascorbate in humans: the dynamic flow model. The model is consistent with previous studies and with the known properties of […]
Read More →
Vitamin C is a reducing substance, an electron donor. When vitamin C donates its two high-energy electrons to scavenge free radicals, much of the resulting dehydroascorbate is rereduced to vitamin […]
Read More →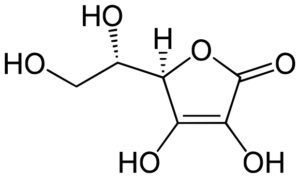
Ascorbic acid or vitamin C is an organic compound from the group of unsaturated polyhydric alcohol. Vitamin C is necessary for the functioning of all living organisms. For many animals […]
Read More →
Vitamin C, also known as L-ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that is naturally present in some foods, added to others, and available as a dietary supplement. Humans, unlike most […]
Read More →
Currently, the recommended upper limit for ascorbic acid (AA) intake is 2000 mg/d. However, because AA is endogenously converted to oxalate and appears to increase the absorption of dietary oxalate, […]
Read More →